Introduction to Remote Sensing
Outline
- Remote Sensing - basic definitions:
- What is Remote Sensing?
- Type of sensors
- Electromagnetic Radiation and its interaction with atmosphere and targets
- Spectral reflectance
- Image properties
- Multispectral imagery
- Satellite data sources
- Copernicus Land Monitoring Service: Global, Pan-European, and Local Components
Learning outcomes
- Get to know the physical concepts of remote sensing
- Familiarized with terms: electromagnetic radiation, spectral reflectance, interaction of electromagnetic radiation with atmosphere and targets
- Learn about image properties, spatial resolution, radiometric resolution, temporal resolution and the spectral characteristics of the Earth’s surface
- Get to know where to look for satellite data
- Get to know about the Copernicus Land Monitoring Service: Global, Pan-European, and Local Components
BoK Concepts
- [GD10-2] Platforms and sensors
- [PP] Physical principles
- [PP1-1] EM radiation
- [PP1-2] Radiation - Matter interaction
- [PS3-4] Properties of digital imagery
What is Remote Sensing?
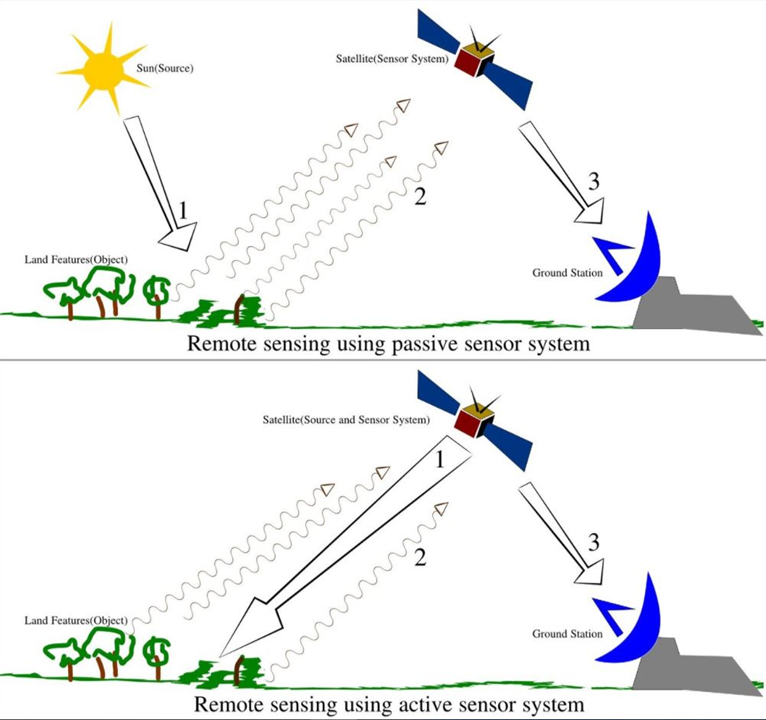
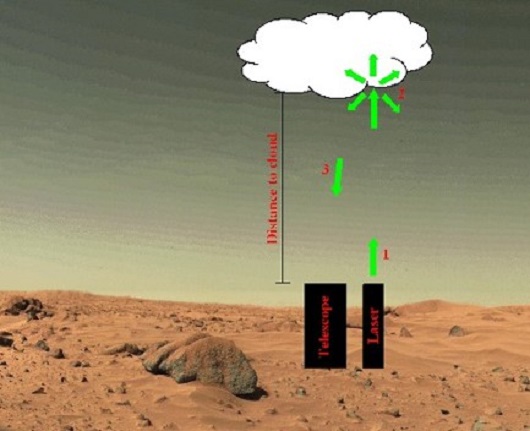
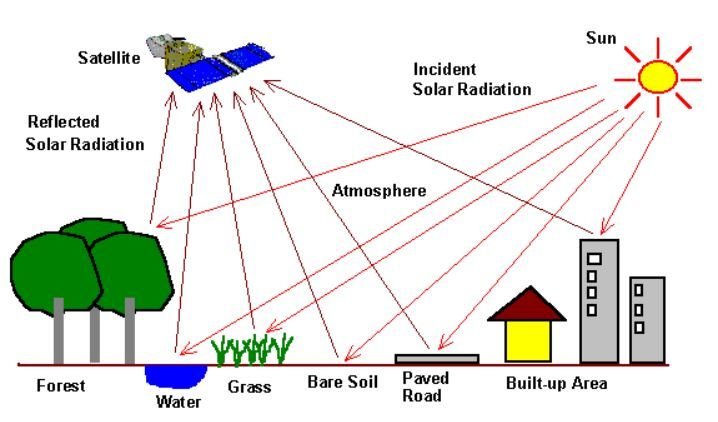
Remote sensing is the collection of information about an object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object.
The sensors must be in some distance from the object.
In our case the object an area of the Earth surface and the sensor is measuring electromagnetic radiation leaving the Earth from a satellite platform.
|

|

|

|
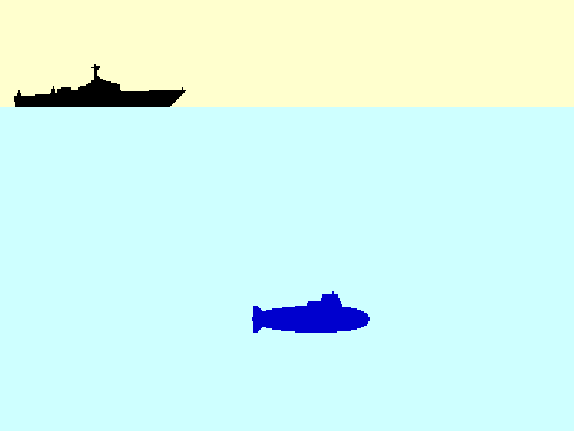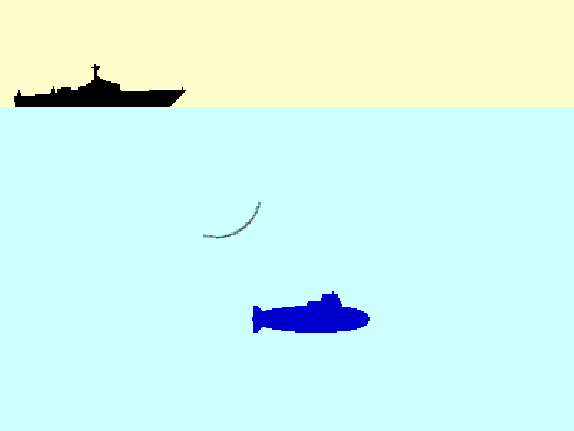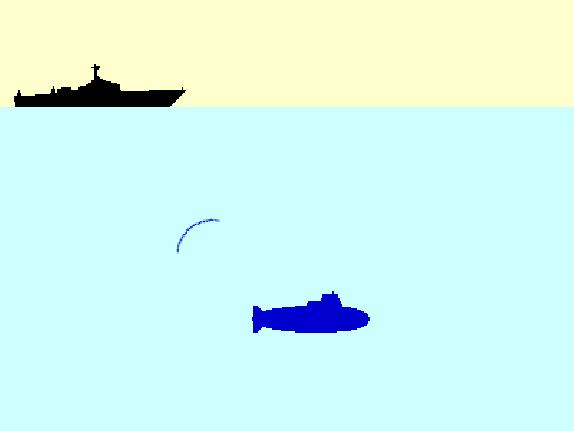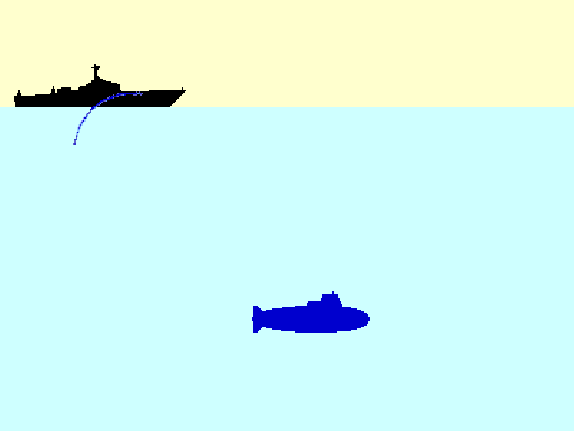
| SONAR (Sound Navigation And Ranging) | LIDAR (LIght Detection And Ranging) | RADAR (RAdio Detection And Ranging) | SPACE Remote Sensing |
What is Remote Sensing?
The remote sensor samples emitted, reflected or scattered electromagnetic radiation (EMR).
Remote Sensing Sensors
- Passive Sensor detects natural energy (radiation) that is emitted or reflected by the object. Reflected sunlight is the primary source of radiation measured by passive sensors, e.g. radiometers.
- Active Sensor generates energy in order to scan objects and areas. The sensor measures the amount of energy returned from the target e.g. synthetic-aperture radar (SAR).
![sat1]()
Arkajun (2013)
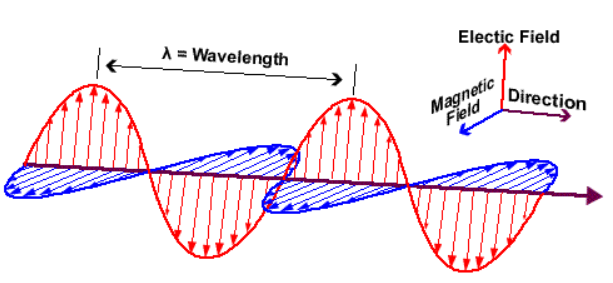
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR)
- wave of the electromagnetic field propagating through space
- travels in a straight line at the speed of light: c = 3 x 108 m/s
- characterized by its frequency (f) and wavelength λ
λ = c / f
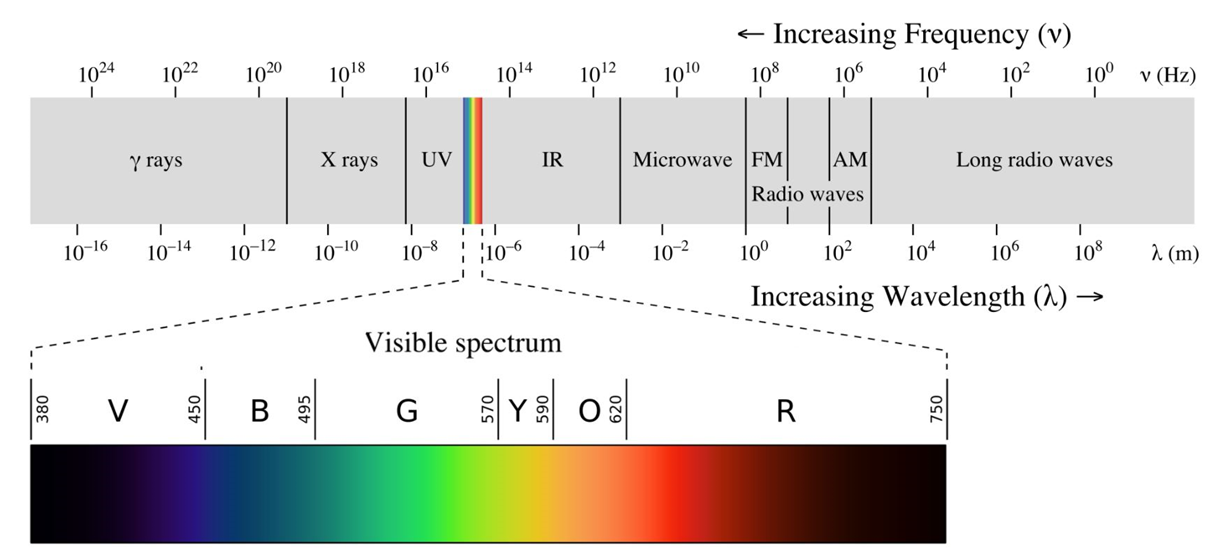
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Electromagnetic radiation is classified by wavelength into gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet, visible, infrared, microwave and radio.
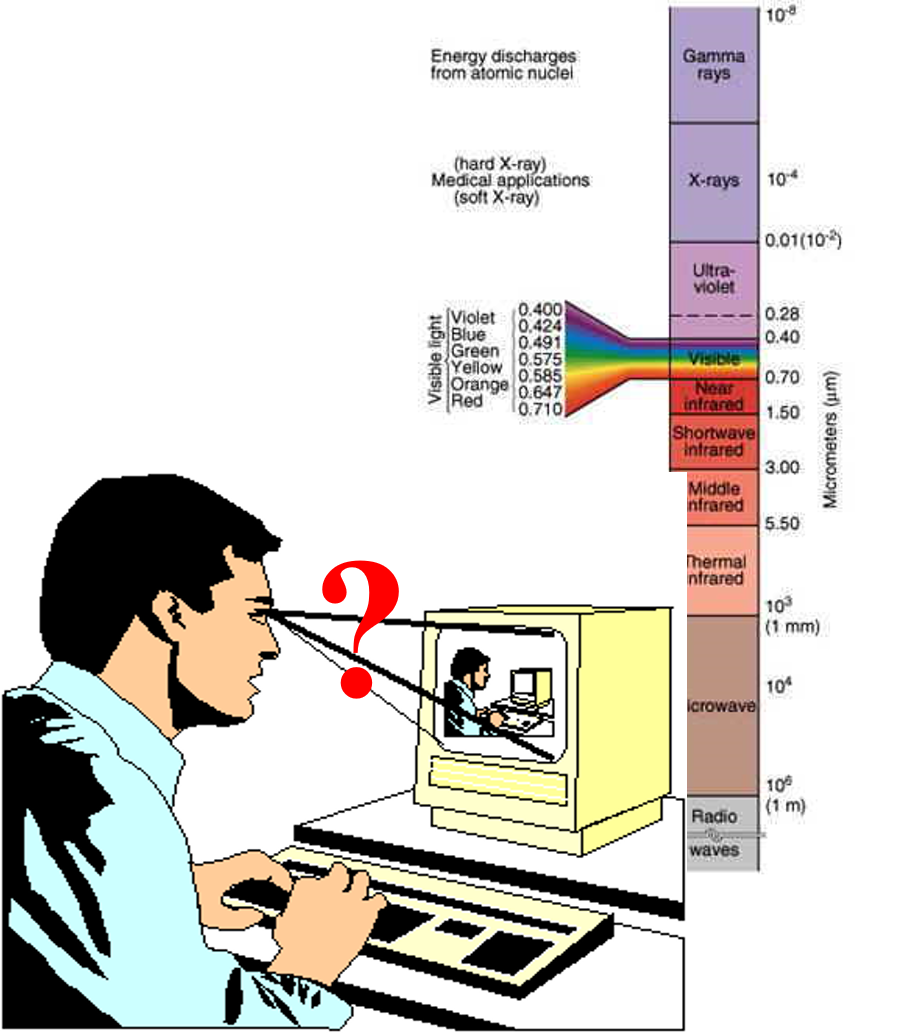
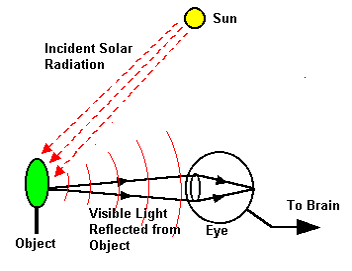
Our daily remote sensing experience in the visible (VIS) spectral range

 -->
-->
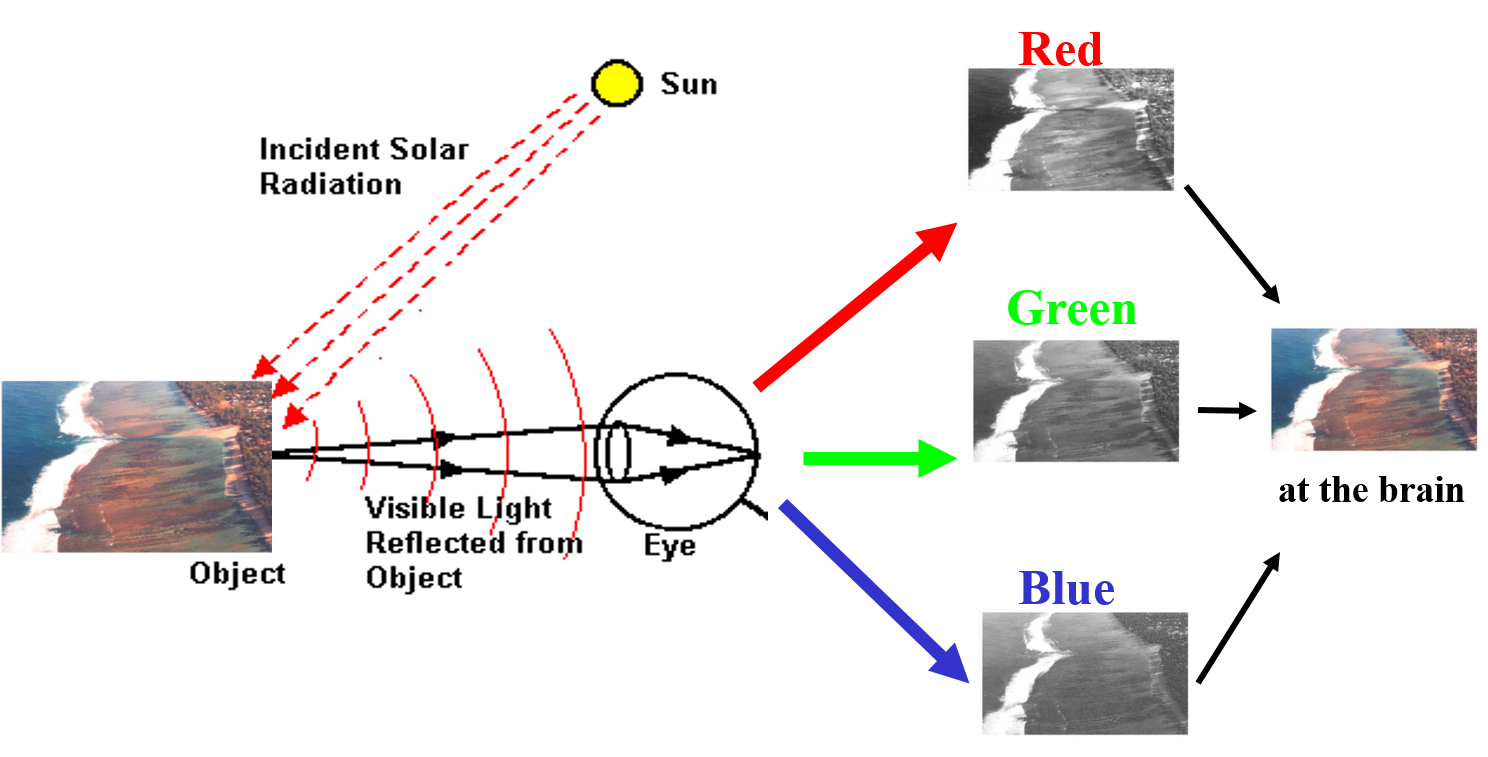
Our daily remote sensing experience
Our daily remote sensing experience
Beyond visible spectral range
Infrared aerial color picture
Interaction of EMR with Atmosphere
Electromagnetic radiation passing through the atmosphere interacts with gas molecules and particulate matter. Effects of interaction:
Atmospheric windows is the area of spectrum not severely influenced by the atmosphere.
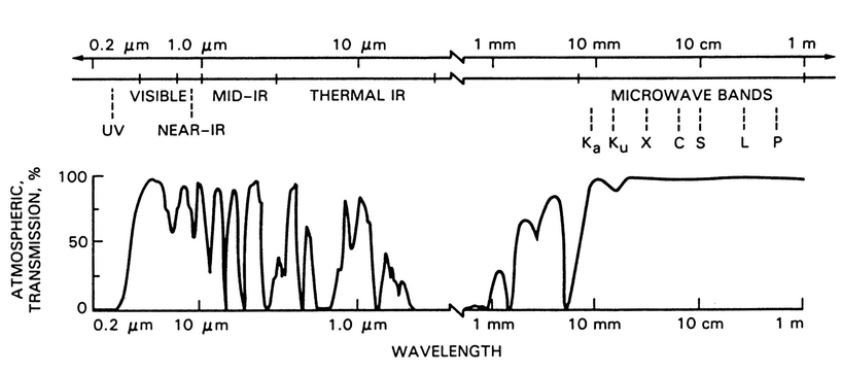
Lewis and Henderson (1998)
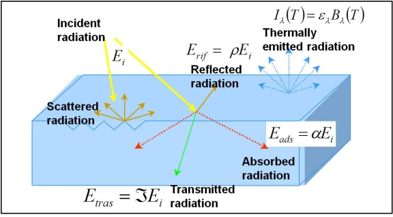
Interaction with target
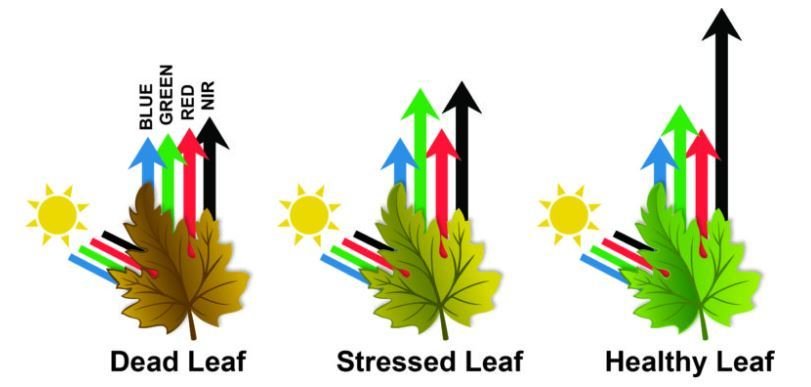
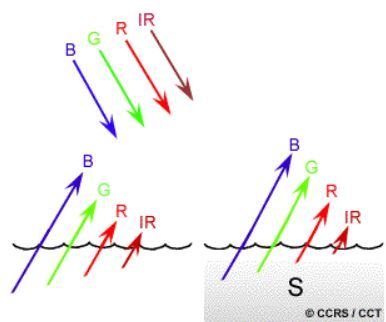
Radiation not absorbed or scattered in the atmosphere can reach and interact with the Earth’s surface.
It can be absorbed by a target, transmitted through a target or reflected. The proportion of each depends on the wavelength and surface features.
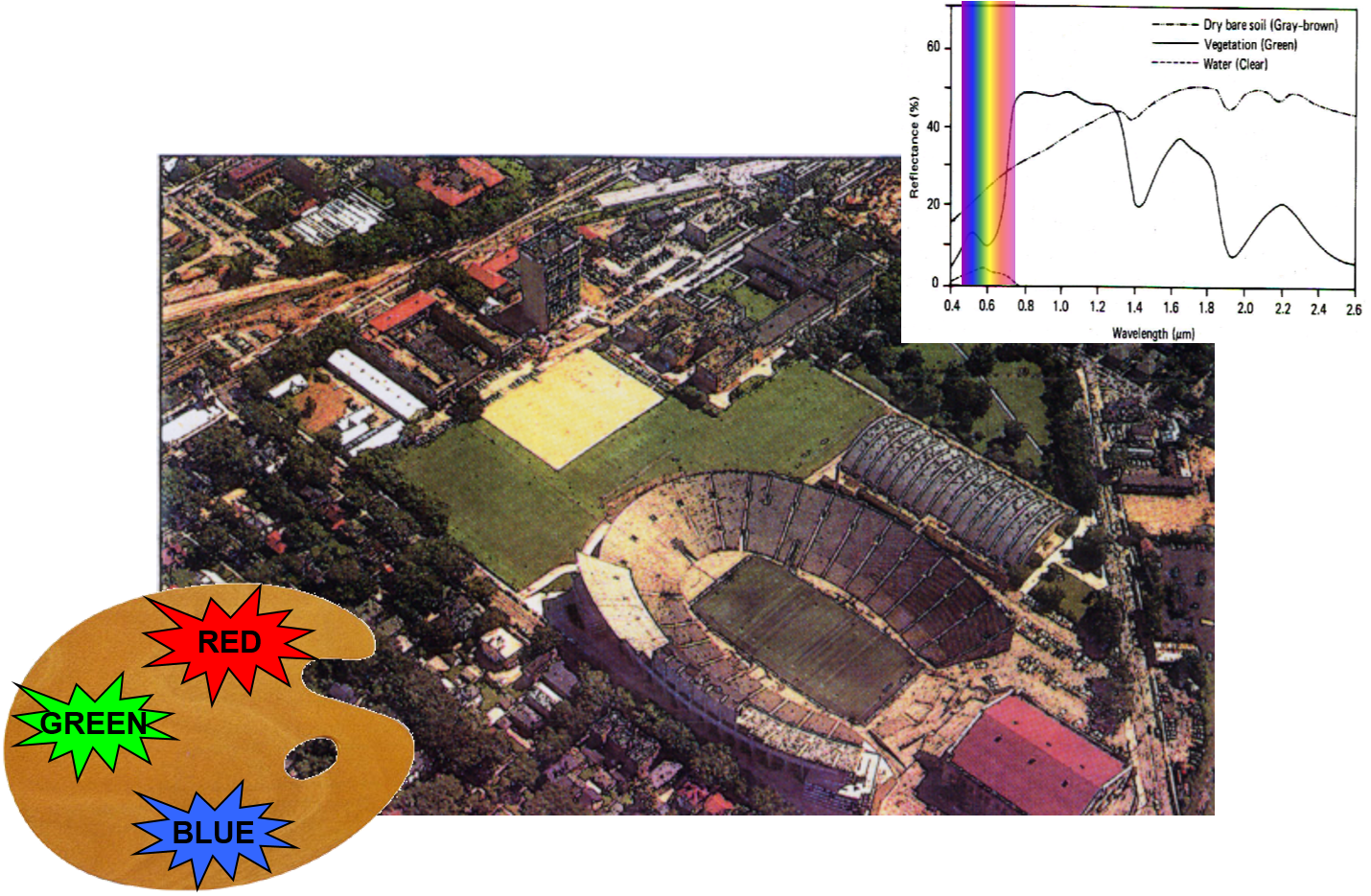
Spectral Reflectance
Spectral Reflectance is the amount of energy reflected from a surface at a specific wavelength. The analysis of the spectral reflectance signatures allows to distinguish different surface feature or materials.
Spectral reflectance curve presents the reflectance of objects as a function of wavelengths.
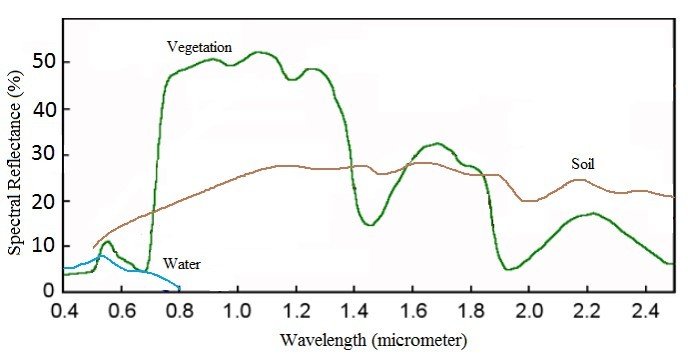
Image Properties
|
Spatial resolution - the size of the smallest area observed on the ground (ground resolution cell) Object is usually detectable if it is equal or larger than the pixel size. The smaller objects could be still detectable as the average brightness of all objects within the pixel. |

|
Image Properties
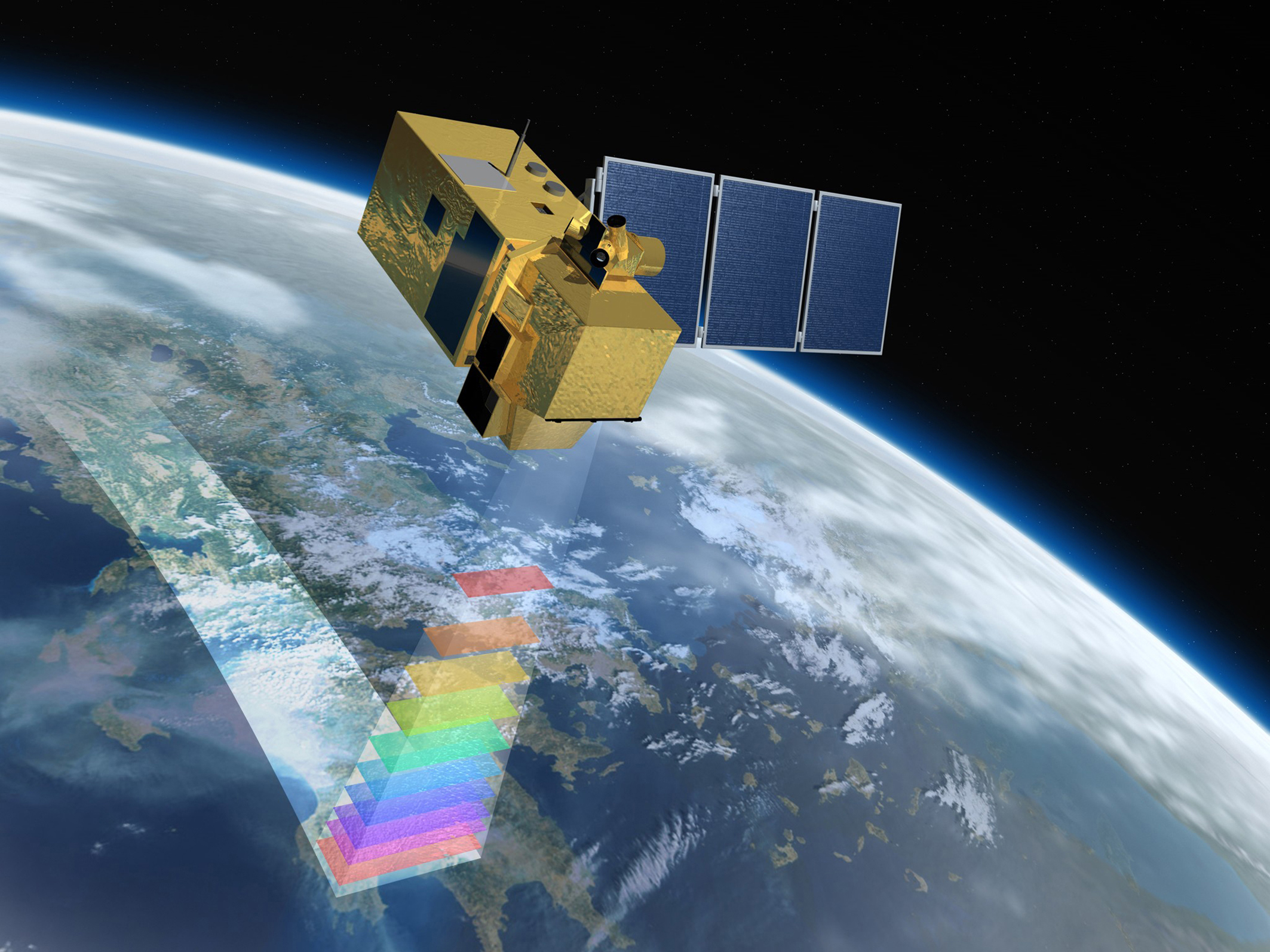
Spectral resolution – refers to the spectral bandwidth and the number of bands.
The finer spectral resolution, the narrower the wavelength range for the particular band.
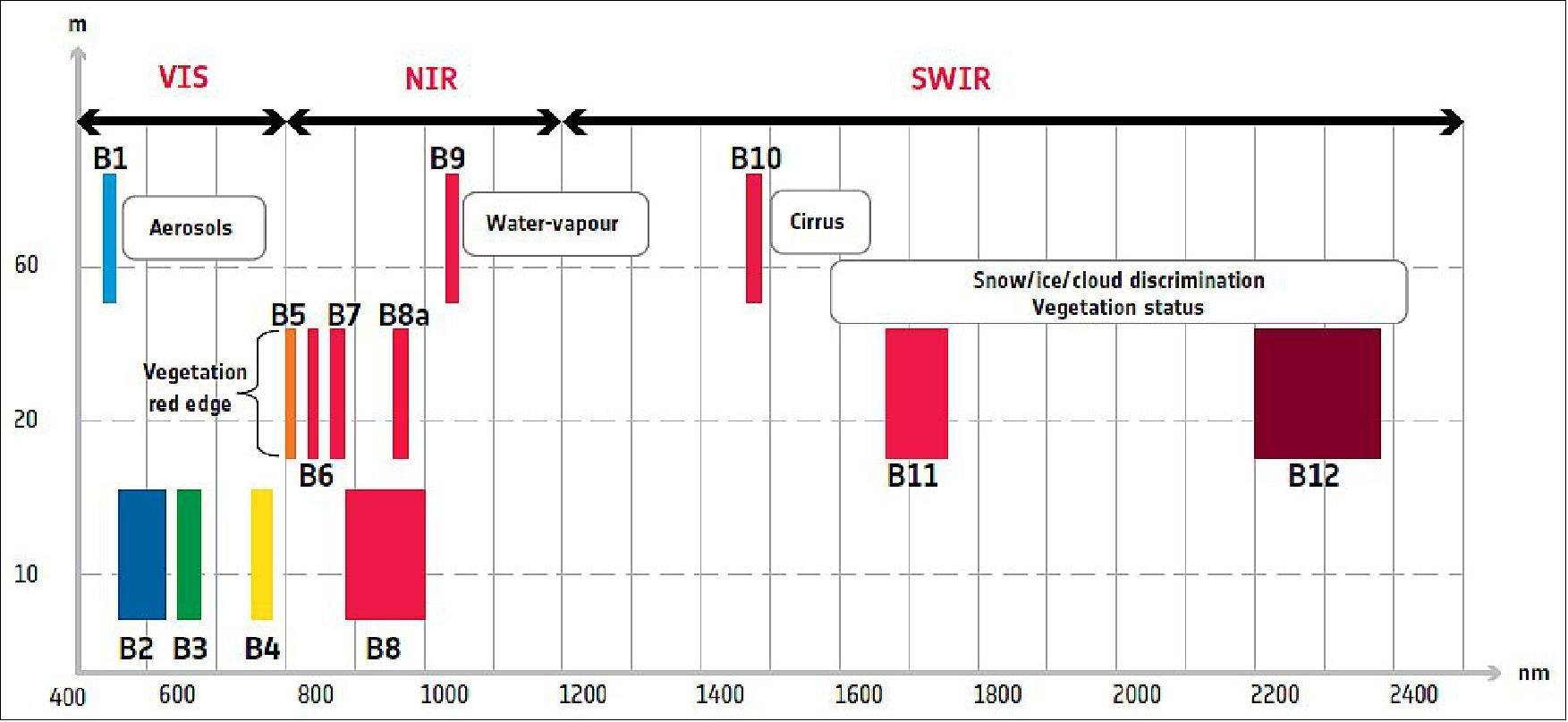
Sentinel-2 spectral characteristics, © ESA
Image Properties
|
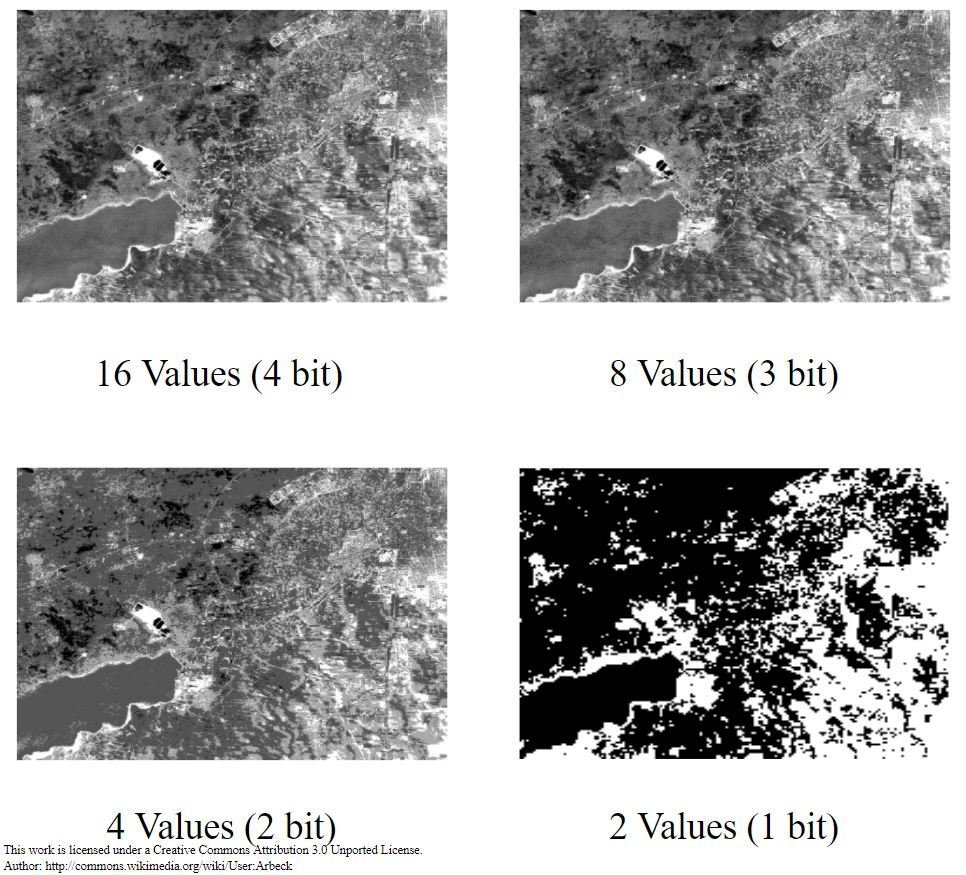
Radiometric resolution - the sensitivity to the magnitude of the electromagnetic energy. It describes the actual information content in an image, expressed in units of bits. The finer the radiometric resolution, the more sensitive it is to detect small differences in reflected or emitted energy. |

|
Image Properties
|
Temporal resolution – frequency at which the same place is observed (revisit capability).
It is particularly important for change mapping. |
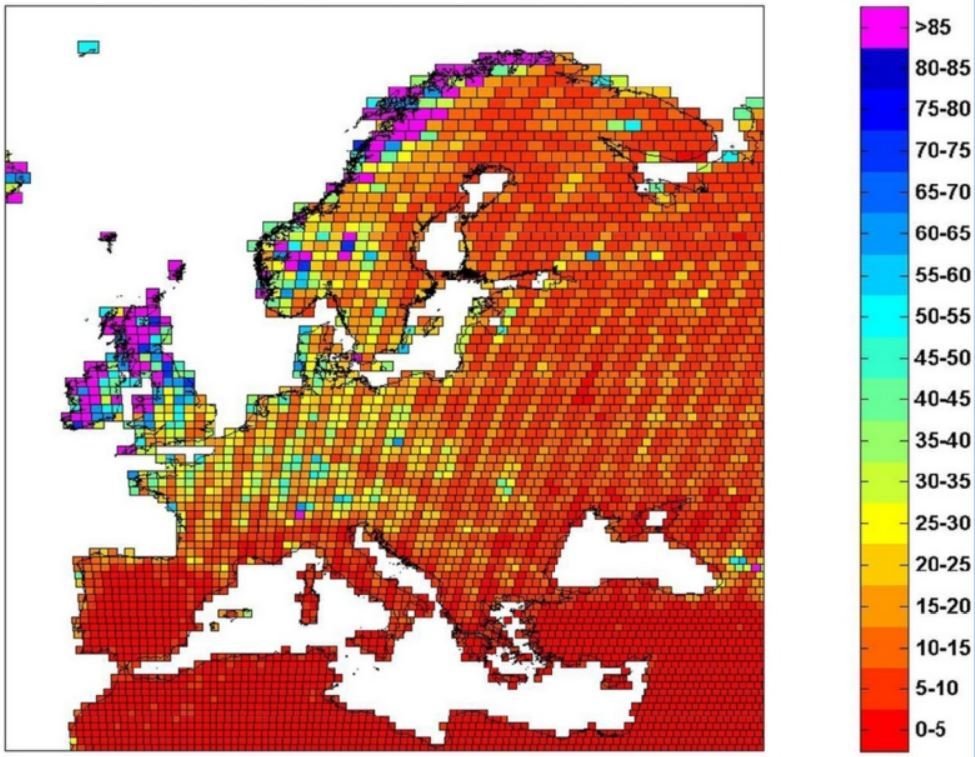
Maximum effective coverage time for Sentinel-2 (days) (<15% cloud cover, 68% confidence) (Spoto et al., 2012). |
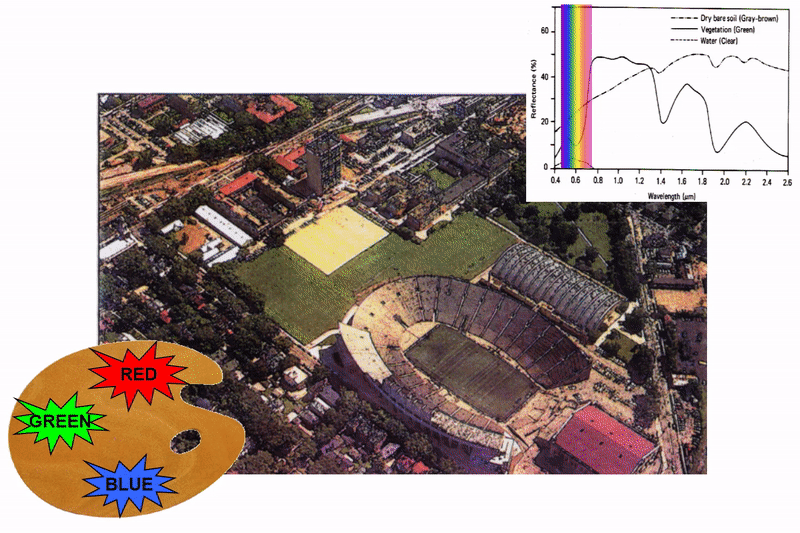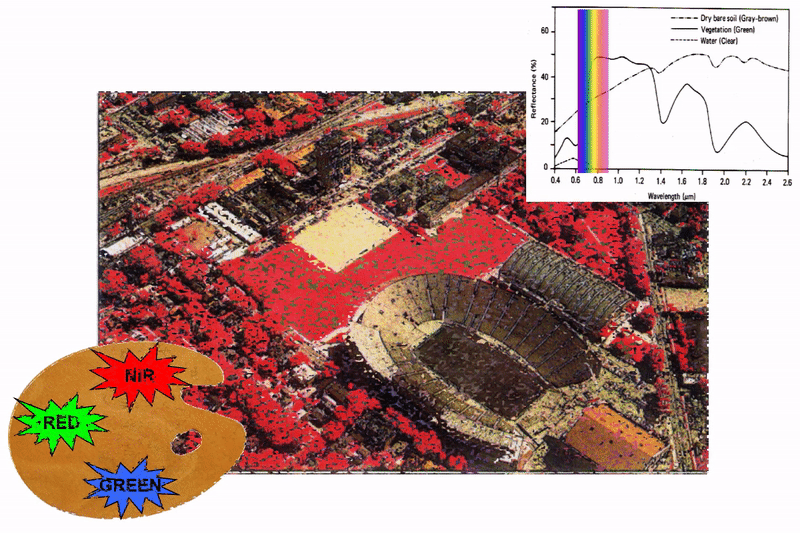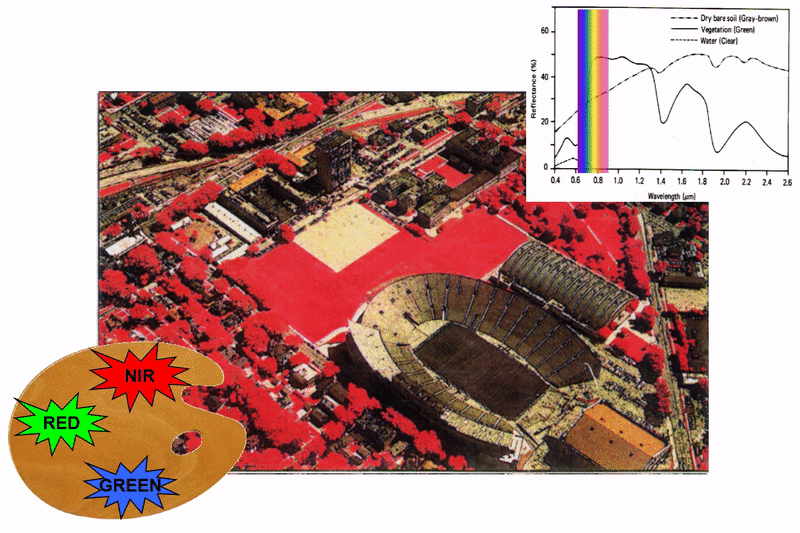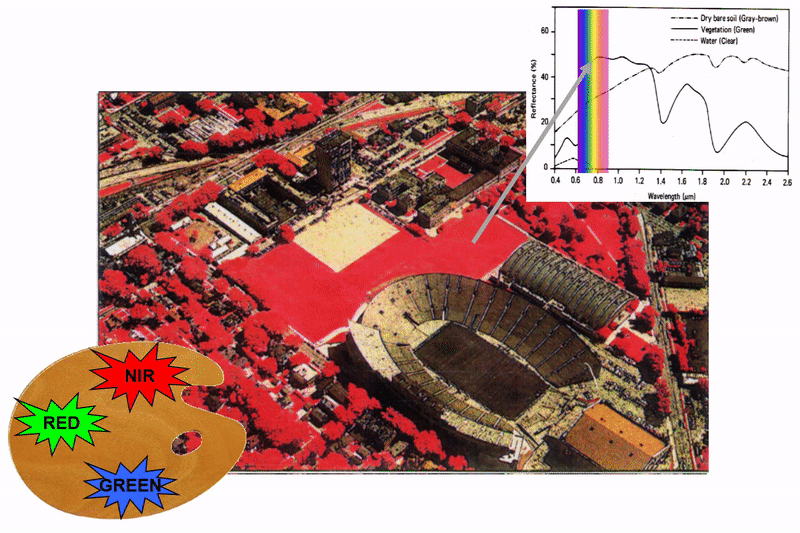
Multispectral imagery
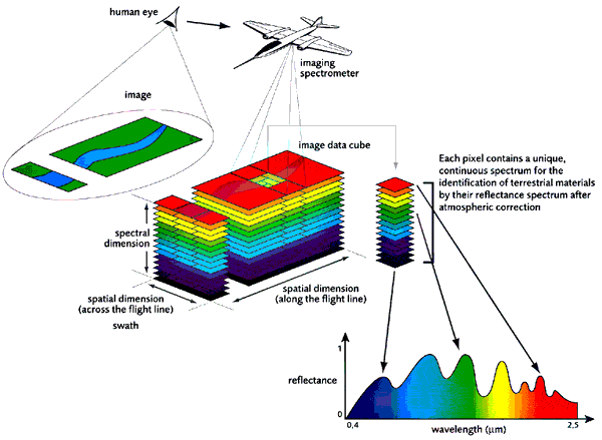
Multispectral imagery
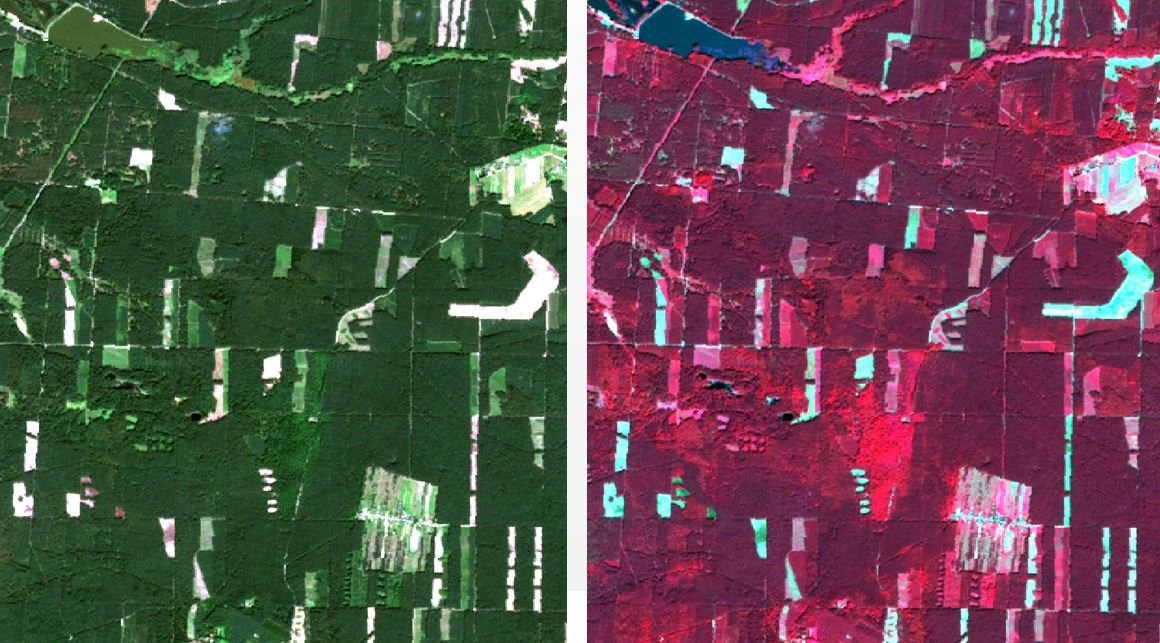
|
natural color composite (R,G,B) |
infrared false color composite (IR,R,G) |

Satellite data source
USGS Earth Explorer
https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/
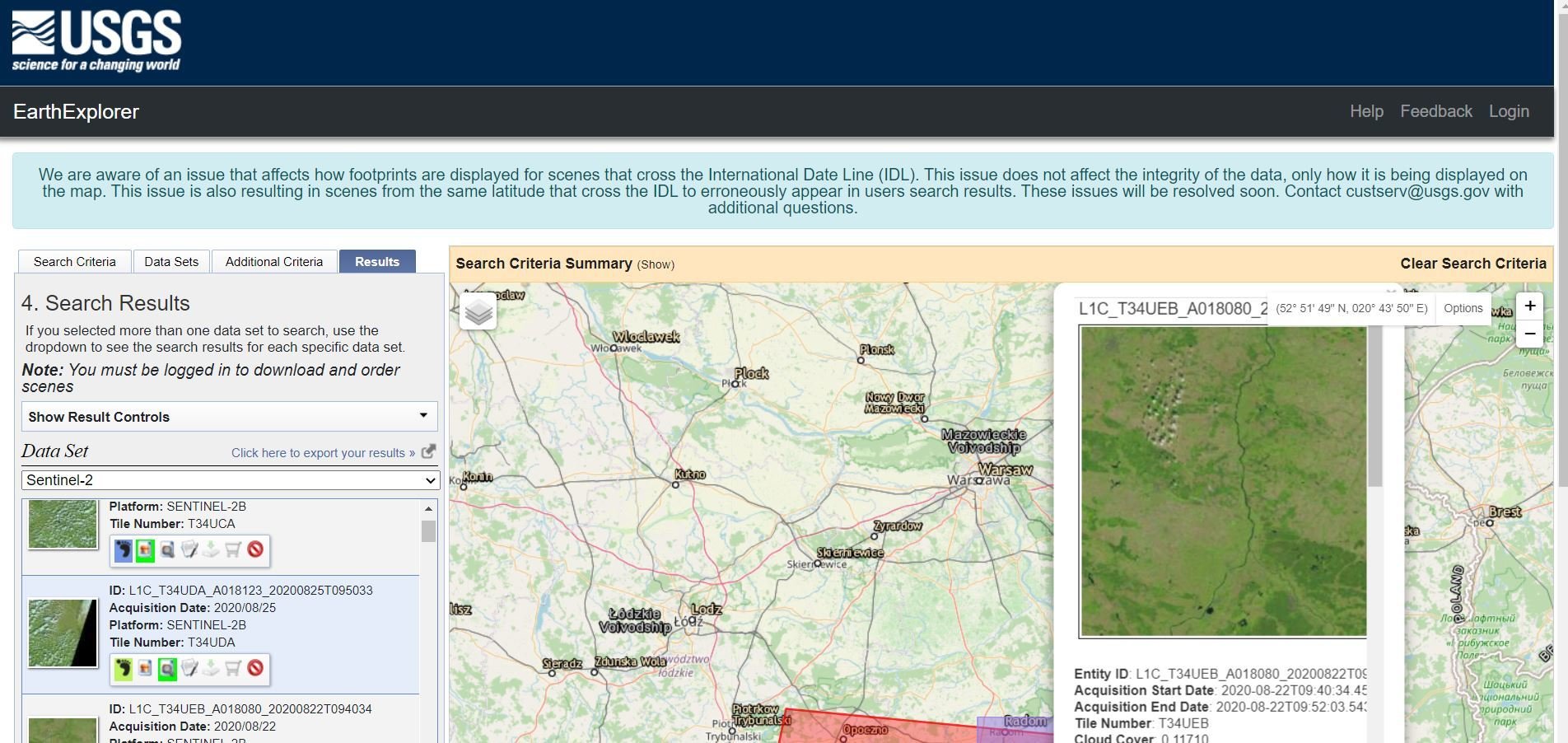
Satellite data source
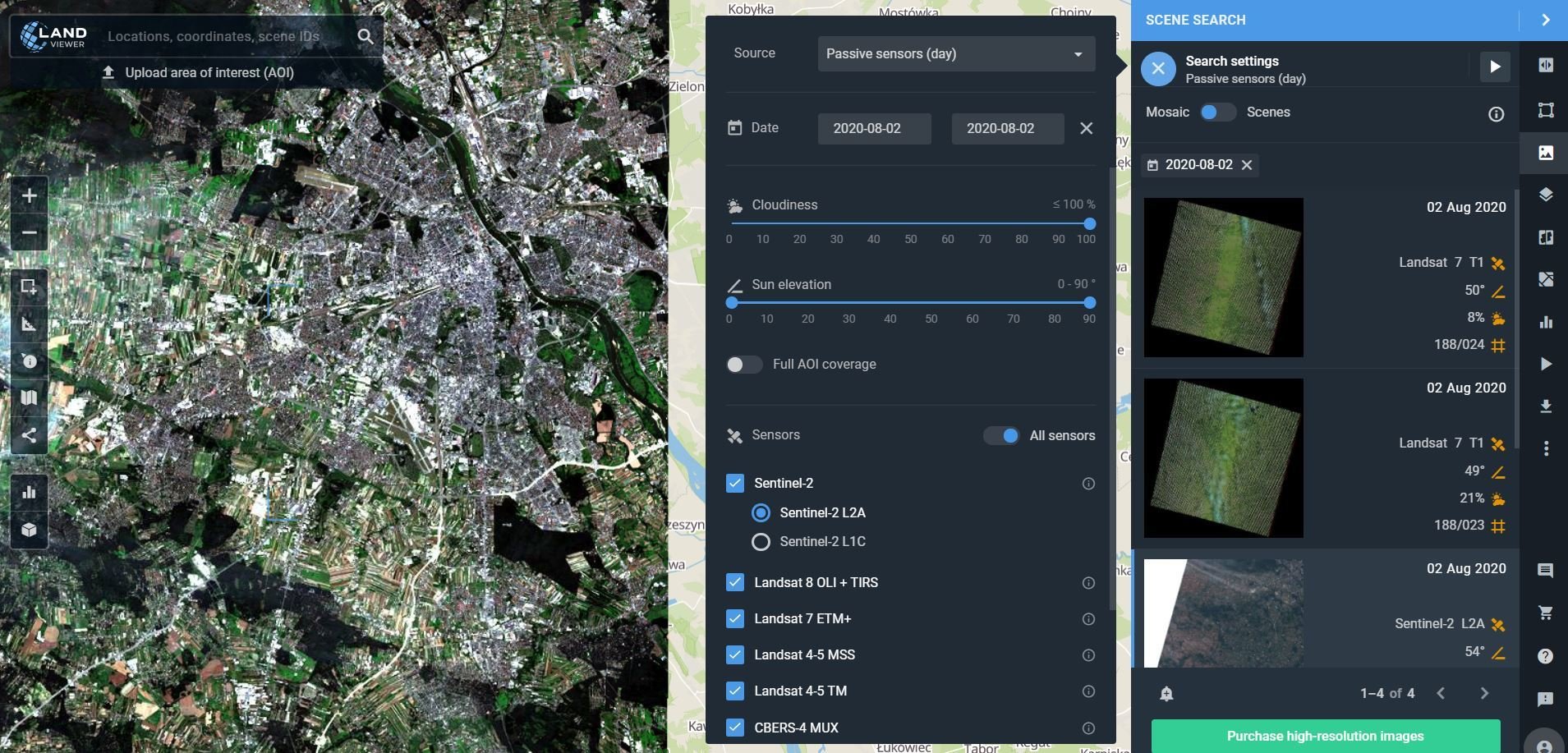
LANDVIEWER
https://eos.com/landviewer/
Satellite data source
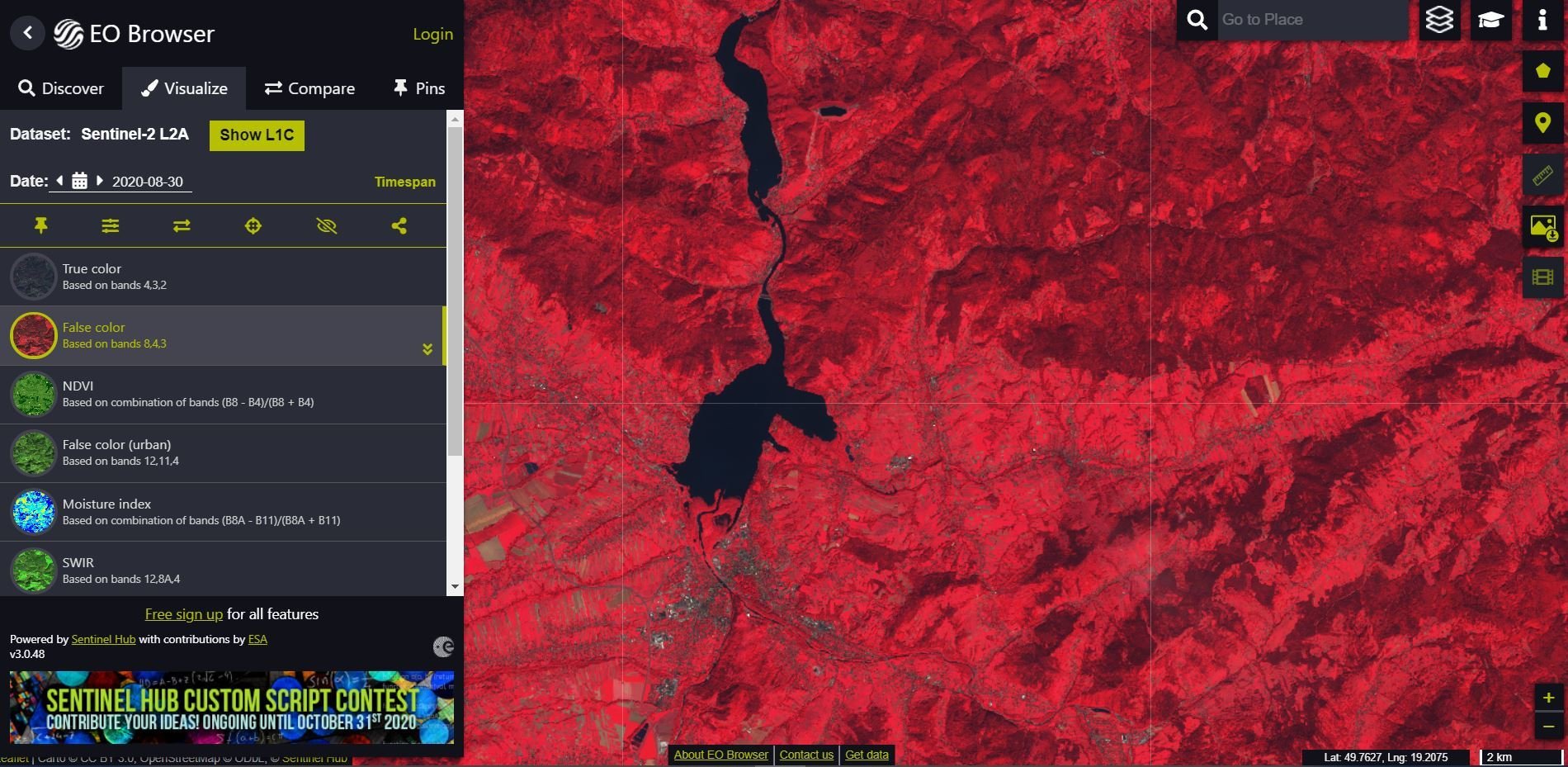
SENTINEL HUB
https://apps.sentinel-hub.com/eo-browser/
Satellite data source
To facilitate and standardise access to data, the European Commission has funded the deployment of five cloud-based platforms called DIAS providing centralised access to Copernicus data and information, as well as to processing tools.
|
All DIAS platforms provide access to Copernicus Sentinel data, as well as to the information products from Copernicus’ six operational services, together with cloud-based tools (open source and/or on a pay-per-use basis). |
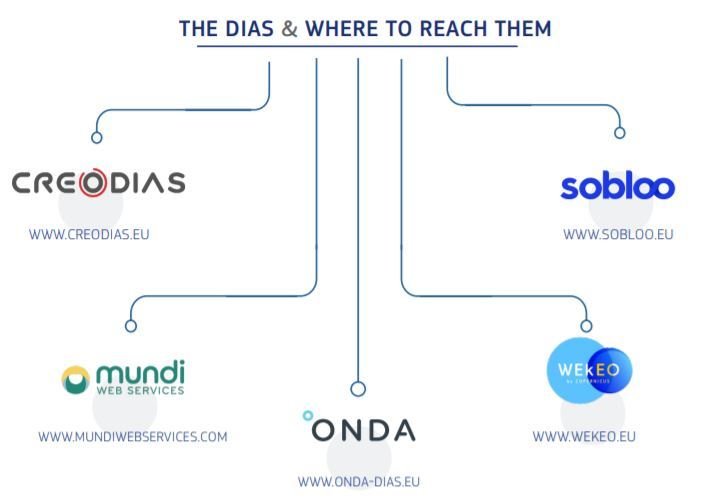
https://www.copernicus.eu/en/access-data/dias source. |
Satellite data source
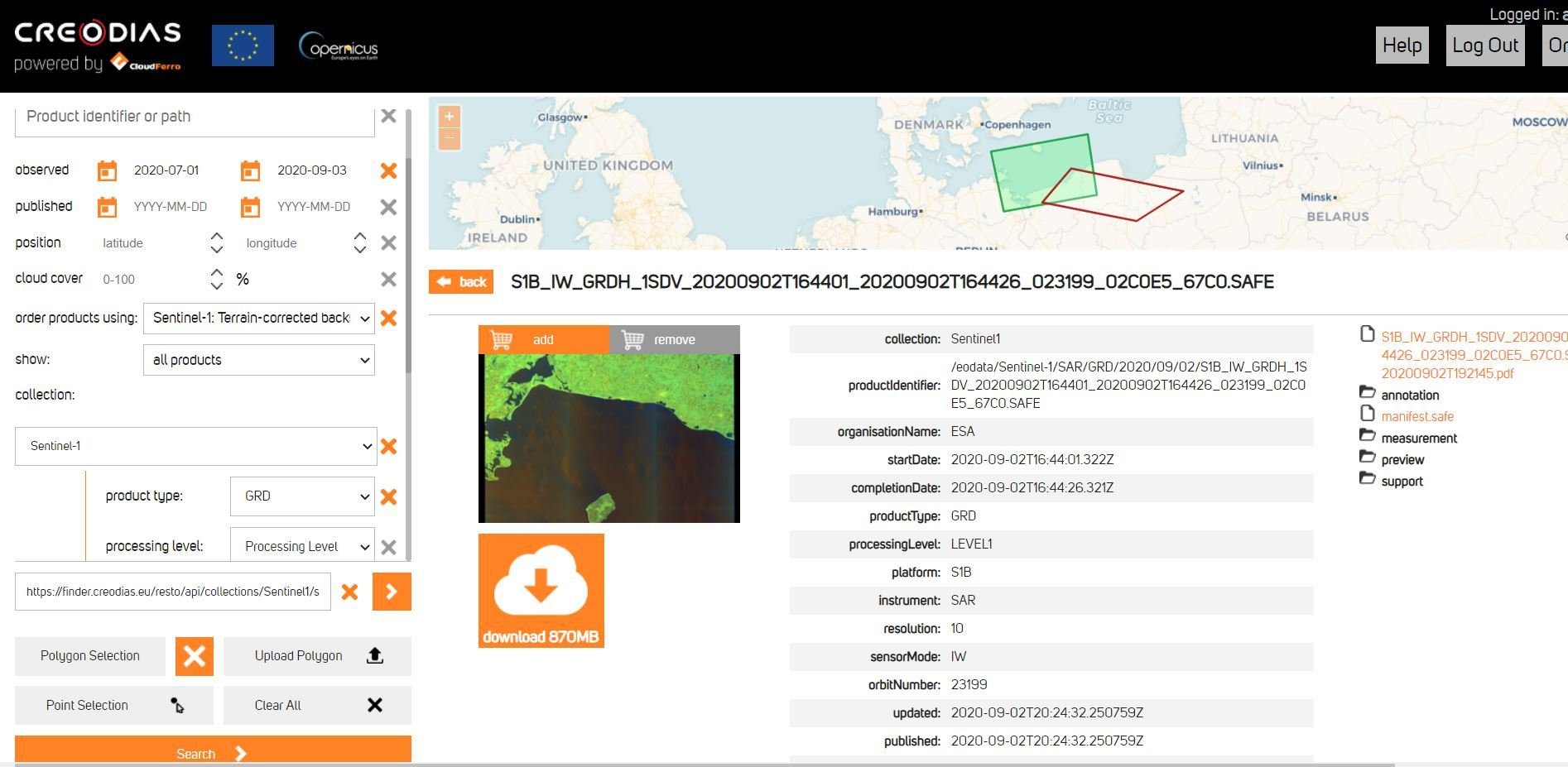
CREODIAS
https://finder.creodias.eu/
Copernicus services
https://www.copernicus.eu/en/services

Copernicus Land Monitoring Service (CLMS)
https://land.copernicus.eu/
Copernicus Global Land Service
https://land.copernicus.eu/global/

CLMS Pan-European component
https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european
CLMS Pan-European component
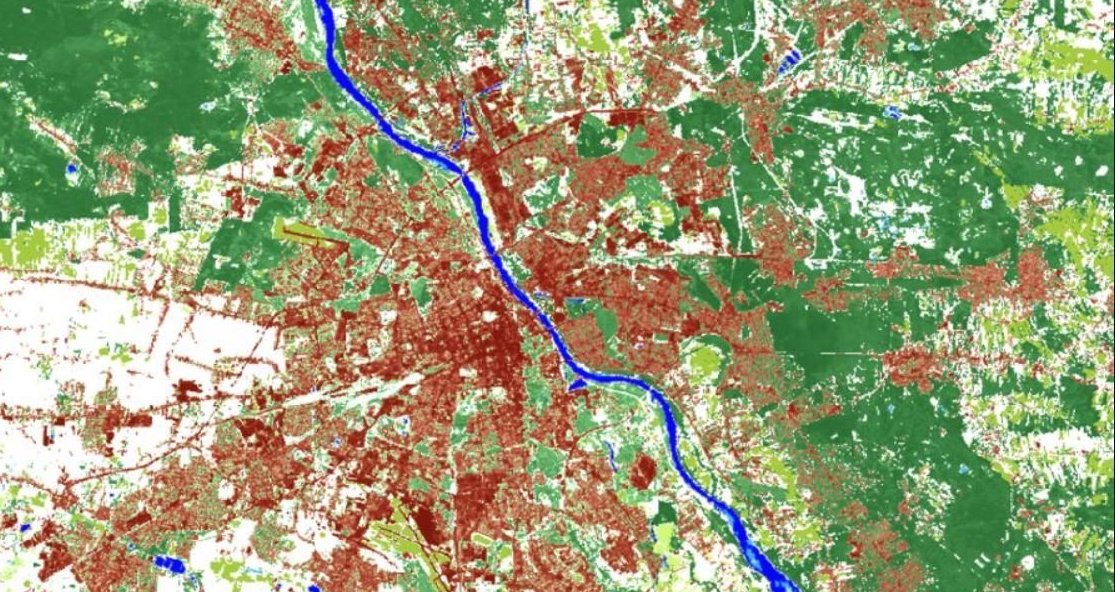
CORINE Land Cover (CLC) inventory was initiated in 1985 (reference year 1990).
Updates produced in 2000, 2006, 2012, and 2018.
|
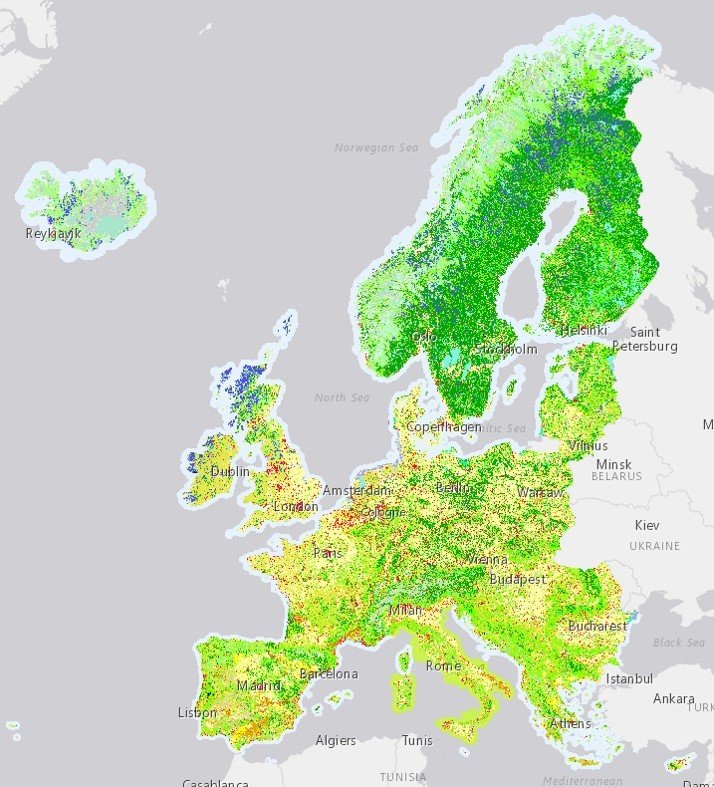
https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/corine-land-cover source. |
CLMS Pan-European component
High Resolution Layers (HRL) provide information on specific land cover characteristics, and are complementary to land cover/land use (LC/LU) mapping such as in the CORINE land cover (CLC) datasets.
Produced from satellite imagery through a combination of automatic processing and interactive rule based classification.

https://land.copernicus.eu/pan-european/high-resolution-layers source.
CLMS Pan-European component
HRL Imperviousness Density and Changes
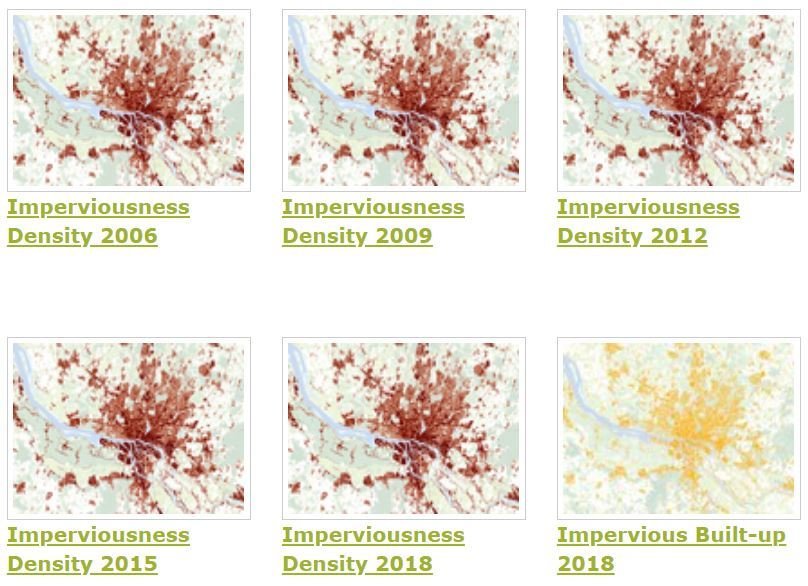
HR Imperviousness Density - status maps source. |
HR Imperviousness - change maps source. |
CLMS Local Component
Local component aims to provide specific and more detailed information that is complementary to the information obtained through the Pan-European component.
There focuses on different hotspots, i.e. areas that are prone to specific environmental challenges and problems. It is based on very high resolution imagery (2,5 x 2,5 m pixels) in combination with other available datasets over the pan-European area.
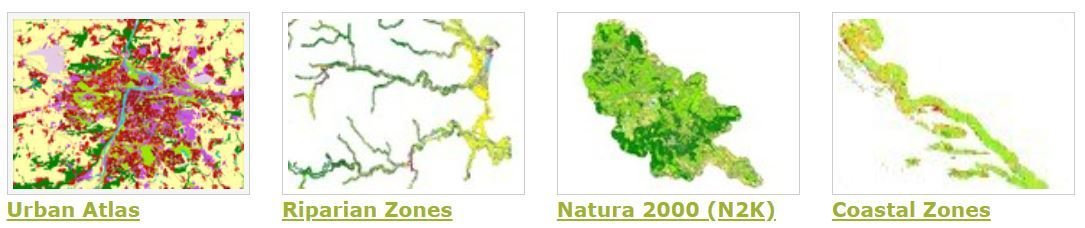
Local component source.
CLMS Local Component
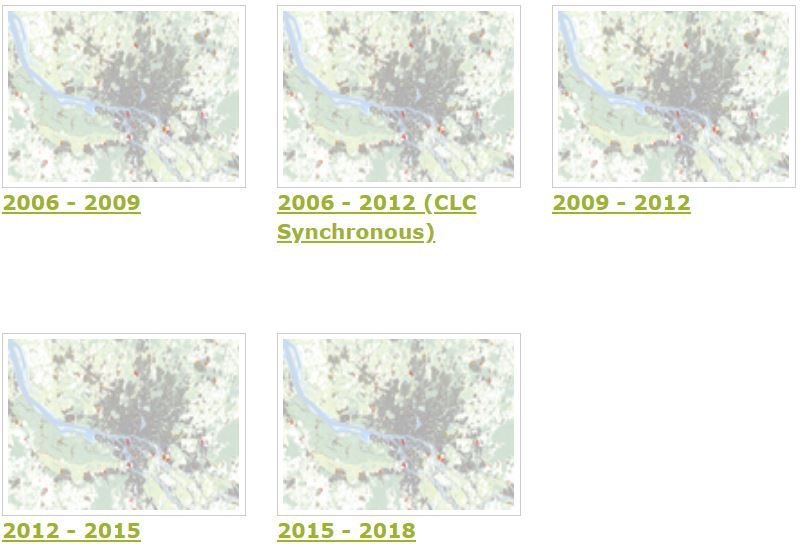
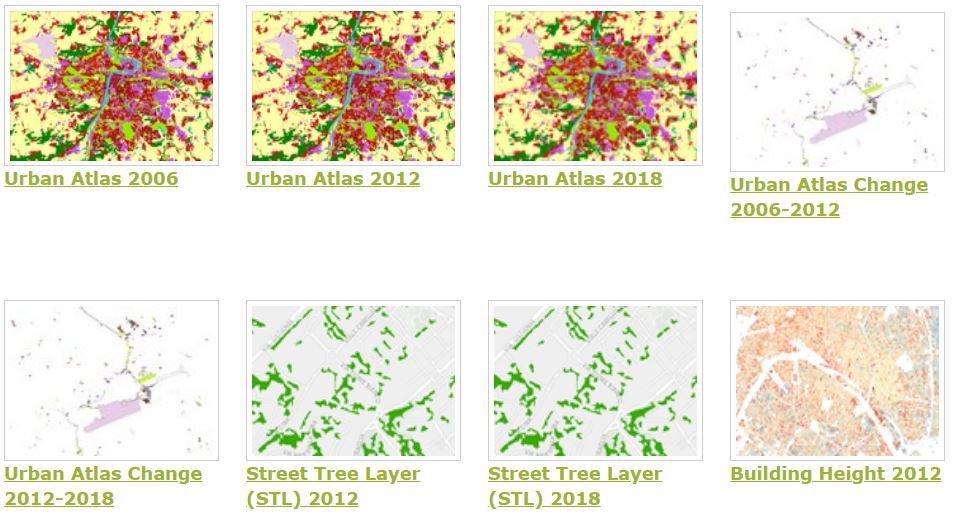
Urban Atlas 2006, 2012 and 2018
785 Functional Urban Areas (FUA) covering EU28 + EFTA countries + West Balkans + Turkey
|
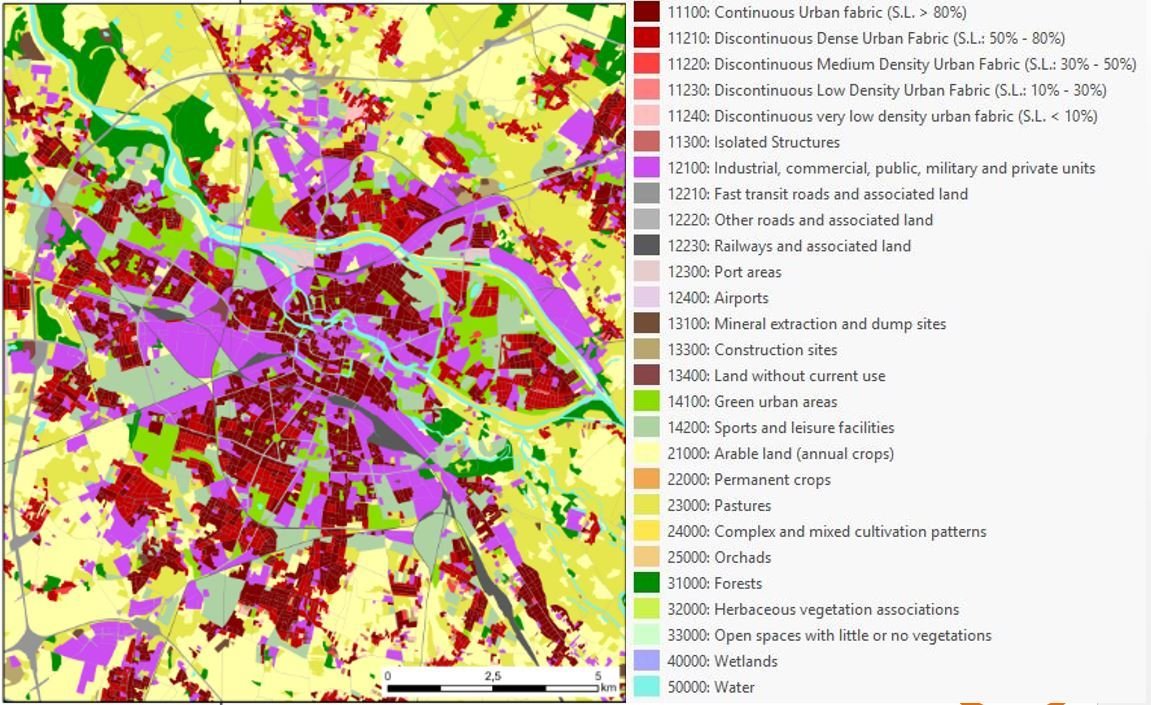
17 Urban LC/LU classes - MMU 0.25 ha 10 Rural LC/LU classes - MMU 1ha |
Urban Atlas source. |
CLMS Local Component
|
|
© IGIK |
CLMS Local Component
Riparian Zones (RZ) represent transitional areas occurring between land and freshwater ecosystems, characterised by distinctive hydrology, soil and biotic conditions and strongly influenced by the stream water.
|
The LC/LU classification is tailored to the needs of biodiversity monitoring in a variable buffer zone of selected rivers (Strahler levels 2-9 derived from EU-Hydro) |
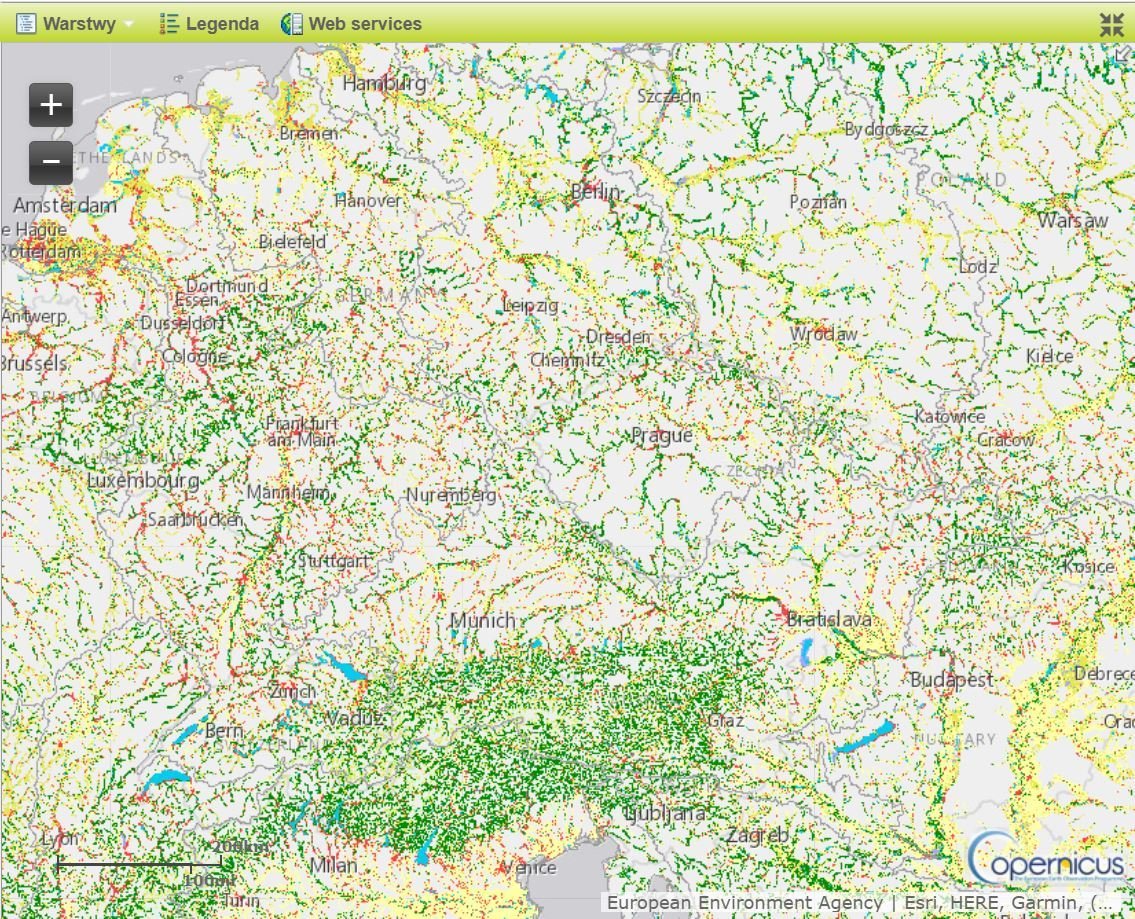
Riparial Zones - Land Cover / Land Use source. |
CLMS Local Component
|
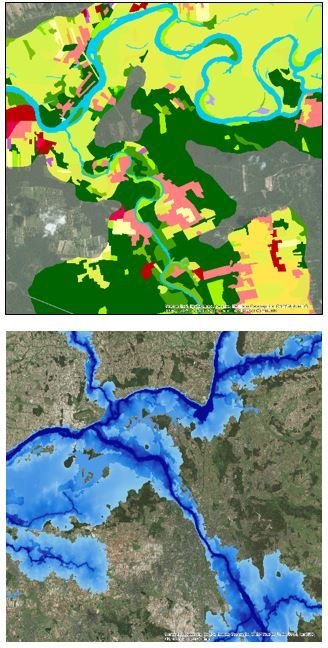
Riparial Zones - Land Cover / Land Use and Delineation of RZ source. |
CLMS Local Component
|
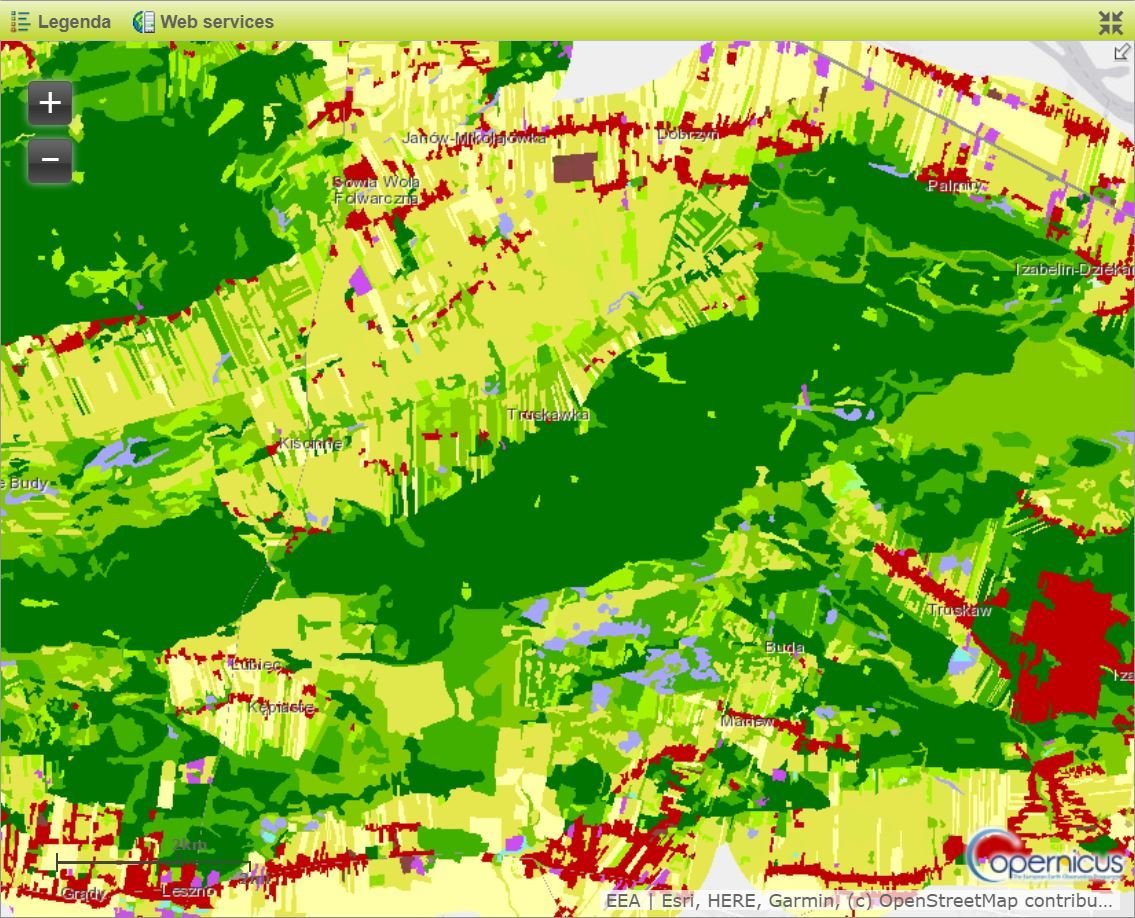
N2K 2012 - Land Cover/Land Use source. |
- A selection grassland-rich sites (chosen within five grassland habitats types: 6210, 6240, 6250, 6510 and 6520).
Approx. 630.000 km2 including a 2km buffer to allow for an analysis of pressures and threats
CLMS Local Component
|
Riparian Zones and Natura2000 nomenclature for Land Cover / Land Use |
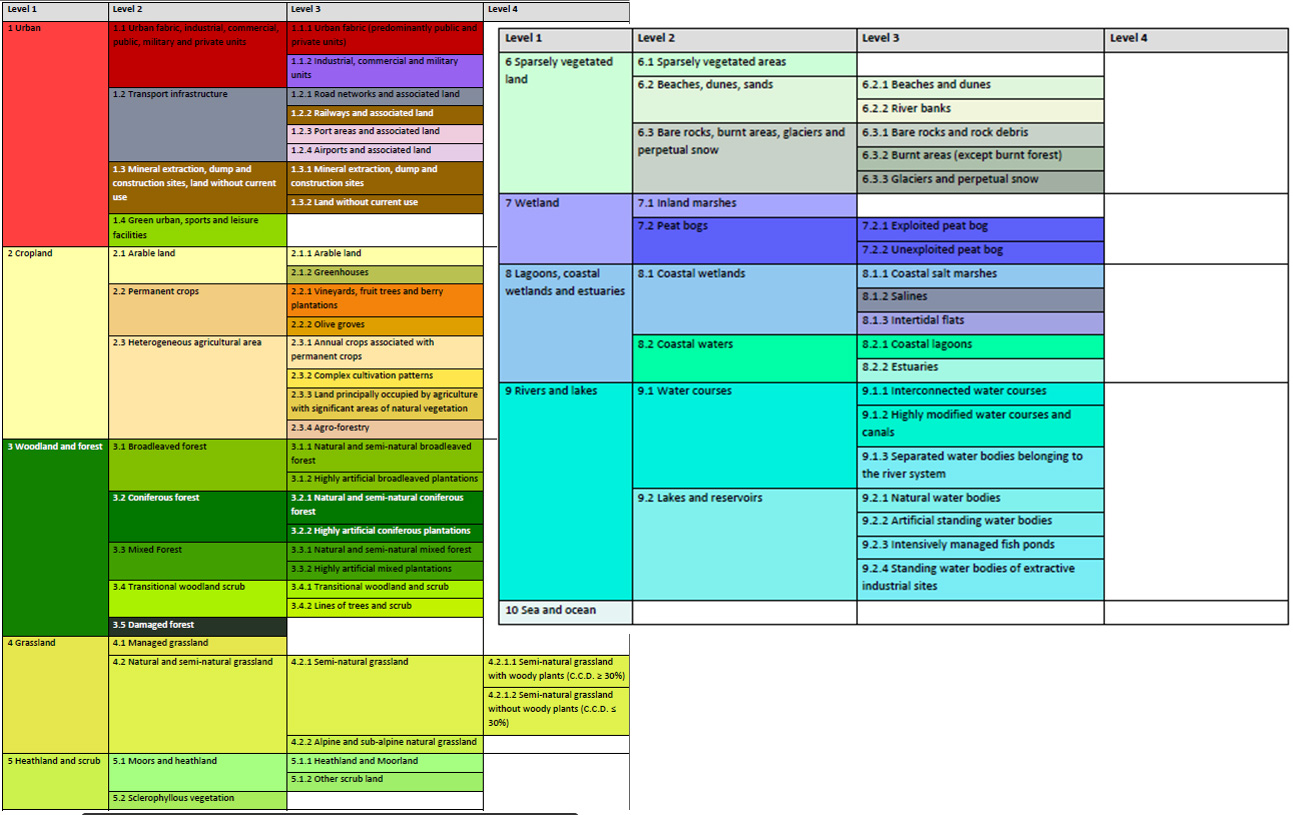
N2K_Nomenclature_Guidelines source. |
CLMS Local Component
|

Coastal Zones source. |
- The map covers a buffer zone of coastline derived from EU-Hydro. LC/LU is extracted from Very High Resolution (VHR) satellite data and other available data.
The class definitions follow the pre-defined nomenclature on the basis of Mapping and Assessment of Ecosystems and their Services (MAES) typology of ecosystems (Level 1 to Level 4) and CORINE Land Cover adapted to the specific characteristics of coastal zones.
CLMS Imagery and reference data
Copernicus land services need both satellite images and in-situ data in order to create reliable products and services.
Imagery and reference data source. |
EU-DEM – pan European digital surface model and EU-Hydro provides a photo-interpreted river network and a modelled drainage network for EEA39 countries. |